
I am currently pursuing a PhD in Computer Science & Engineering at Indian Institute of Technology Jodhpur. My research focuses on Natural Language Processing and Computer Vision.
I design methods for contextual text error correction in Indic languages, multi-modal knowledge extraction, and low-resource learning.
Warning
Problem: The current name of your GitHub Pages repository ("Solution: Please consider renaming the repository to "
http://".
However, if the current repository name is intended, you can ignore this message by removing "{% include widgets/debug_repo_name.html %}" in index.html.
Action required
Problem: The current root path of this site is "baseurl ("_config.yml.
Solution: Please set the
baseurl in _config.yml to "Education
-
 Indian Institute of Technology JodhpurComputer Science & Engineering
Indian Institute of Technology JodhpurComputer Science & Engineering
Ph.D. Student2020 - 2026 (expected) -
 University of HyderabadM.Tech. in Information Technology2017 - 2019
University of HyderabadM.Tech. in Information Technology2017 - 2019 -
 Government Engineering College AjmerB.Tech. in Information Technology2012 - 2016
Government Engineering College AjmerB.Tech. in Information Technology2012 - 2016
News
Selected Publications (view all )
Post-ASR Correction for Low-Resource Rajasthani Language
Abhishek Bhandari and Gaurav Harit
ACM Transactions on Asian and Low-Resource Language Information Processing (TALLIP)
State-of-the-art multilingual Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) models produce systematic errors when applied to lowresource languages like Rajasthani, for which they lack dedicated training data. This paper addresses this challenge by introducing a post-ASR correction framework that leverages the complementary error patterns in the outputs (termed as views) from two distinct models: Whisper-large-v3 and MMS-1B-All. We propose a multi-view1, character-level sequence-tosequence (Seq2Seq) model that uses a gated fusion mechanism to dynamically weigh information from the two ASR outputs. On a new benchmark created from the IndicTTS Rajasthani corpus, our gated model achieves a Character Error Rate (CER) of 7.86% and a Word Error Rate (WER) of 29.98%. This outperforms the best single-view baselines (8.01% CER and 30.33% WER), simple multi-view concatenation (8.21% CER and 30.05% WER), as well as Llama-3.2-3B and mBART-50-large, both fine-tuned on Whisper and MMS inputs. It also surpasses powerful Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4o and Gemini 2.5 Pro in a zero-shot setting. This work establishes the first baseline for post-ASR correction in Rajasthani, demonstrating that a compact, specialized model is more effective than general-purpose LLMs for this targeted, low-resource task.
Post-ASR Correction for Low-Resource Rajasthani Language
Abhishek Bhandari and Gaurav Harit
ACM Transactions on Asian and Low-Resource Language Information Processing (TALLIP)
State-of-the-art multilingual Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR) models produce systematic errors when applied to lowresource languages like Rajasthani, for which they lack dedicated training data. This paper addresses this challenge by introducing a post-ASR correction framework that leverages the complementary error patterns in the outputs (termed as views) from two distinct models: Whisper-large-v3 and MMS-1B-All. We propose a multi-view1, character-level sequence-tosequence (Seq2Seq) model that uses a gated fusion mechanism to dynamically weigh information from the two ASR outputs. On a new benchmark created from the IndicTTS Rajasthani corpus, our gated model achieves a Character Error Rate (CER) of 7.86% and a Word Error Rate (WER) of 29.98%. This outperforms the best single-view baselines (8.01% CER and 30.33% WER), simple multi-view concatenation (8.21% CER and 30.05% WER), as well as Llama-3.2-3B and mBART-50-large, both fine-tuned on Whisper and MMS inputs. It also surpasses powerful Large Language Models (LLMs) like GPT-4o and Gemini 2.5 Pro in a zero-shot setting. This work establishes the first baseline for post-ASR correction in Rajasthani, demonstrating that a compact, specialized model is more effective than general-purpose LLMs for this targeted, low-resource task.
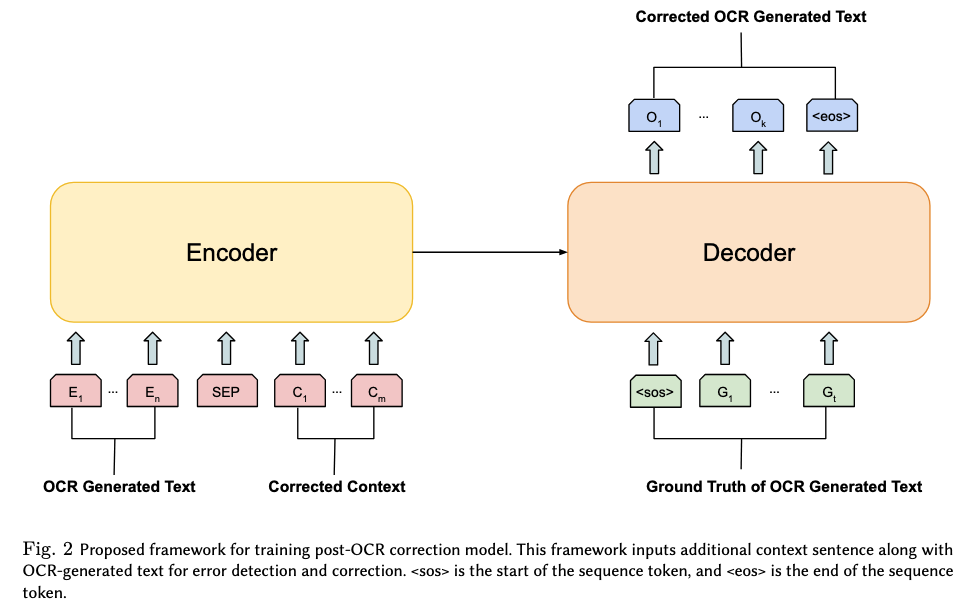
A Framework and Dataset for Contextual Post-OCR Correction
Abhishek Bhandari and Gaurav Harit
Accepted in ACM Transactions on Asian and Low-Resource Language Information Processing (TALLIP)
This paper presents a framework and dataset for contextual post-OCR correction to improve text quality in low-resource and noisy OCR settings.
A Framework and Dataset for Contextual Post-OCR Correction
Abhishek Bhandari and Gaurav Harit
Accepted in ACM Transactions on Asian and Low-Resource Language Information Processing (TALLIP)
This paper presents a framework and dataset for contextual post-OCR correction to improve text quality in low-resource and noisy OCR settings.
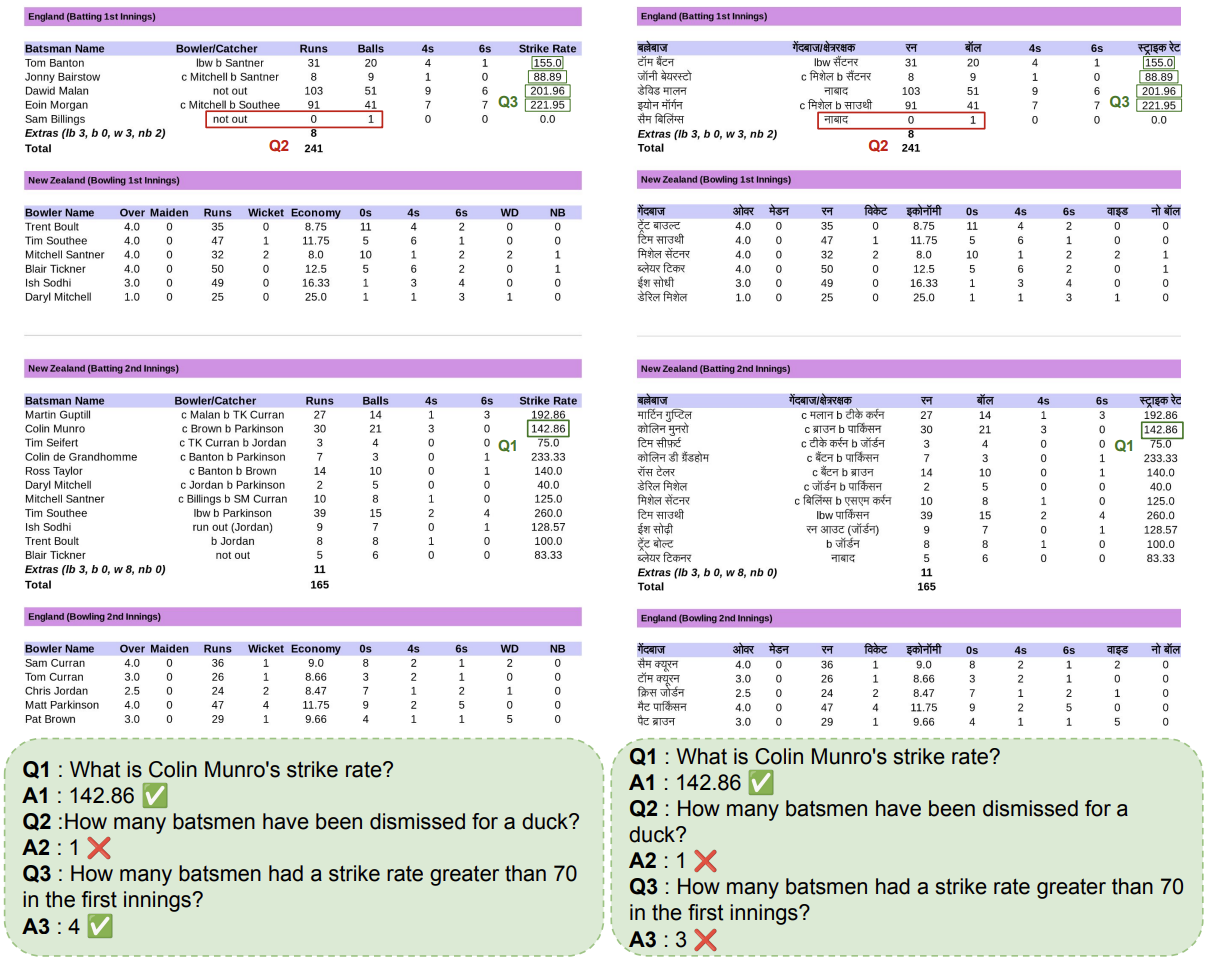
Mind the (Language) Gap: Towards Probing Numerical and Cross-Lingual Limits of LVLMs
Somraj Gautam, AS Penamakuri, Abhishek Bhandari, Gaurav Harit
Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Multilingual Representation Learning (MRL 2025)
This paper introduces MMCRICBENCH-3K, a benchmark for Visual Question Answering on cricket scorecards designed to evaluate large vision-language models on complex numerical and cross-lingual reasoning over semi-structured tabular images. Empirical results show that state-of-the-art models struggle with structure-aware numerical reasoning and cross-lingual generalization.
Mind the (Language) Gap: Towards Probing Numerical and Cross-Lingual Limits of LVLMs
Somraj Gautam, AS Penamakuri, Abhishek Bhandari, Gaurav Harit
Proceedings of the 5th Workshop on Multilingual Representation Learning (MRL 2025)
This paper introduces MMCRICBENCH-3K, a benchmark for Visual Question Answering on cricket scorecards designed to evaluate large vision-language models on complex numerical and cross-lingual reasoning over semi-structured tabular images. Empirical results show that state-of-the-art models struggle with structure-aware numerical reasoning and cross-lingual generalization.
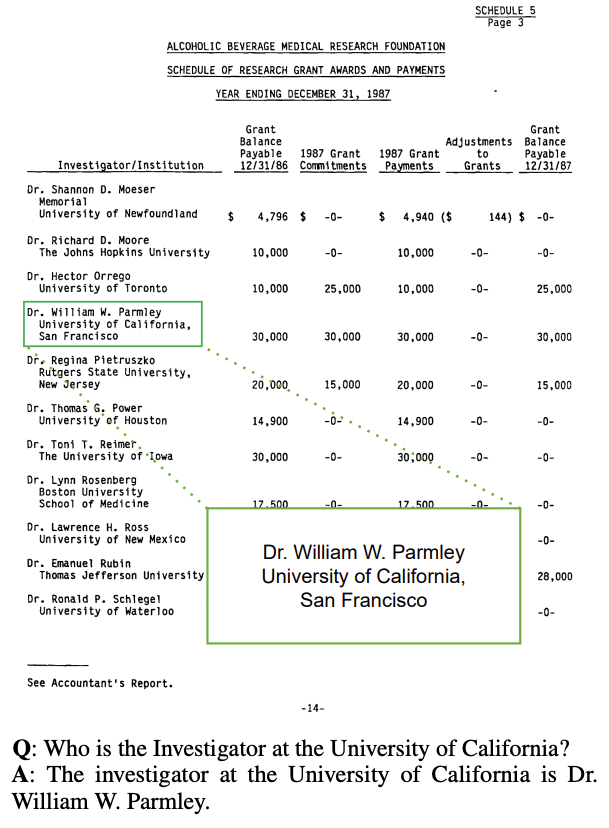
TabComp: A Dataset for Visual Table Reading Comprehension
Somraj Gautam, Abhishek Bhandari, Gaurav Harit
Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: NAACL 2025
This paper introduces TabComp, a dataset for visual table reading comprehension. The dataset is designed to advance research in understanding and extracting information from tables in documents.
TabComp: A Dataset for Visual Table Reading Comprehension
Somraj Gautam, Abhishek Bhandari, Gaurav Harit
Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: NAACL 2025
This paper introduces TabComp, a dataset for visual table reading comprehension. The dataset is designed to advance research in understanding and extracting information from tables in documents.
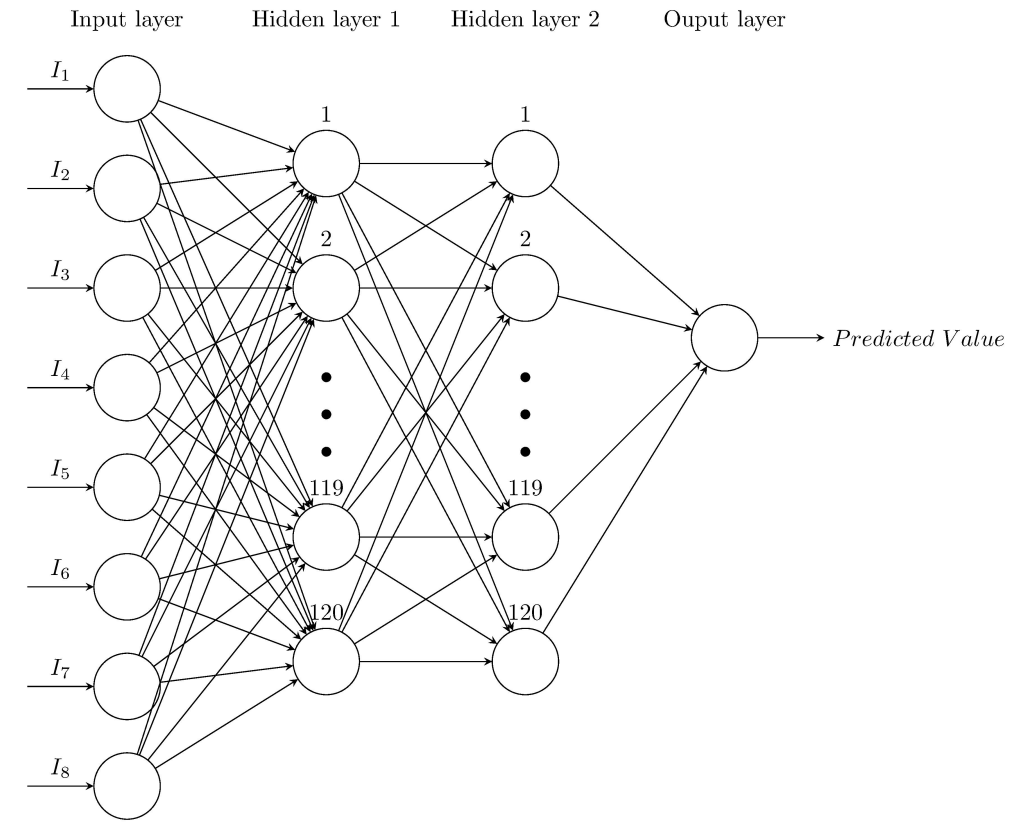
Reversible data hiding using multi-layer perceptron based pixel prediction
A Bhandari, S Sharma, R Uyyala, R Pal, M Verma
Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Advances in Information Technology 2020
This paper presents a novel approach for reversible data hiding using multi-layer perceptron for pixel prediction. Reversible data hiding is a technique that allows the original cover media to be perfectly restored after the hidden data has been extracted.
Reversible data hiding using multi-layer perceptron based pixel prediction
A Bhandari, S Sharma, R Uyyala, R Pal, M Verma
Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Advances in Information Technology 2020
This paper presents a novel approach for reversible data hiding using multi-layer perceptron for pixel prediction. Reversible data hiding is a technique that allows the original cover media to be perfectly restored after the hidden data has been extracted.